Unlocking the Power of Unlimited Residential Proxies: Scale Without Limits
In‑depth 2025 guide to unlimited residential proxies: features, use cases, top providers, and best practices for reliable, large-scale operations.
Apr 11, 2025
Learn what CAPTCHA is, how it works, how to solve it correctly, and how residential proxies can help reduce challenges.
Ever been asked to type twisted letters or pick out traffic lights in a grid online? That’s a CAPTCHA! These little tests stop bots from messing up websites, but they can trip up regular users, too. In this guide, we’ll explain what CAPTCHAs are, how they work, and how to solve them easily—plus tips for proxy users to avoid them!

CAPTCHA stands for "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart." It’s a website security measure to prevent bots from abusing services. The idea came from researchers at Carnegie Mellon University in 2003, inspired by the Turing test (a famous challenge to see if machines can act human). Here, the goal is the opposite—proving you’re not a bot.
Classic text CAPTCHAs distort letters and numbers so humans can read them, but OCR bots struggle with segmentation and holistic parsing. Image CAPTCHAs ask you to select specific objects—like traffic lights or crosswalks—something bots still struggle with.
The latest reCAPTCHA doesn’t even ask you questions. Instead, it watches how you move your mouse or tap the screen. For example, humans wiggle their cursor a bit or scroll naturally, while bots might zip in straight lines or click too fast. It gives you a score (0.0 to 1.0) to decide if you’re legit.
Once you submits a response, the server validates it by checking against known patterns or cryptographic tokens. If you fail, the site might show a tougher CAPTCHA or block you temporarily to keep bots out.
CAPTCHA challenges are issued when a site’s security systems detect anomalous or high-risk traffic patterns. Common triggers include:
Stopping Spam: They block bots from posting junk comments or fake sign-ups.
Boosting Security: CAPTCHAs protect against hackers trying to guess passwords automatically.
Keeping Data Real: They make sure website info (like survey answers) comes from humans, not robots.
Fun Fact: Early CAPTCHAs helped digitize old books by having users type out scanned words—pretty cool, right?
1. Text-Based CAPTCHA: Users are prompted to type distorted letters or numbers displayed in an image. Used because it’s simple, but bots are catching up.

2. Image Recognition CAPTCHA: Users identify specific objects within a set of images, such as selecting all squares containing traffic lights. Tougher for bots, easy if you can see well.

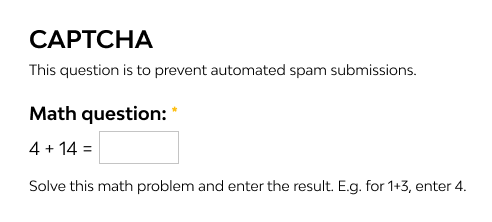
3. Math Problems: Simple arithmetic questions like “2 + 3 = ?” Quick for humans, tricky for basic bots.
4. reCAPTCHA: Developed by Google, it offers both visible challenges and invisible assessments based on user behavior. Super common and smart!
5. hCAPTCHA: Like reCAPTCHA but with a focus on images—and it might pay website owners a little.

Here’s how to ace those tests every time, with tips for each type:
Match Case Exactly: If the puzzle shows uppercase or lowercase letters, mirror that precisely to avoid errors. If it’s “AbC,” type “AbC”—don’t guess!
Refresh When Needed: If the distortion is too heavy, click the refresh icon for a clearer one.
Editor’s Tip: Avoid using copy/paste—type manually to reduce format issues.
Follow Instructions Precisely: Click every square with the object (like all the crosswalk bits).
Check-and-Uncheck Trick: Selecting all required images, then toggling an extra tile, can signal a human’s indecision to the system.
Editor’s Tip: If it’s blurry or slow, refresh or check your connection.
Audio Challenges: Use headphones in noisy environments; play the audio multiple times if needed.
Math Prompts: Perform simple arithmetic accurately; ensure numeric entry format matches (e.g., “5” not “five”).
Screen-Reader Compatibility: Ensure the CAPTCHA offers ARIA labels or alternative text for visually impaired users.
Keyboard Navigation: Use tab/enter keys for selection where possible.
Important: Only bypass CAPTCHAs with permission (e.g., for testing or approved data tasks). Unauthorized bypassing can break laws or site rules.
Rotate IPs: Distribute requests across thousands of residential IPs to avoid looking like a bot—like calling from different phones.
Rotate User Agents: Vary browser fingerprints to prevent fingerprint-based detection.
Captcha Resolvers: Platforms like 2Captcha or Anti-Captcha use human workers to solve challenges in real time, returning tokens for automated submission.
Browser Extensions: Tools like Buster solve audio CAPTCHAs using speech-to-text for quicker human-in-loop resolution.
Human-Like Delays: Insert random pauses (2–5 s) between actions to mimic human reading and clicking behavior.
Realistic Mouse Movements: Emulate realistic mouse paths instead of straight-line movements, as Google’s invisible CAPTCHA tracks cursor trajectories.
Think of proxies as costumes for your internet connection. They make each request look like it’s from a new person, helping you dodge CAPTCHA triggers.
Proxies aren’t perfect. If you don’t act human (like moving your mouse right), smart CAPTCHAs can still spot you.
1. Use High-Quality Residential Proxies: These proxies route traffic through real devices, making them less detectable.
2. Implement Human-Like Interaction Patterns: Incorporate random delays, mouse movements, and varied browsing paths.
3. Limit Request Frequency: Avoid sending too many requests in a short time frame from the same IP.
CAPTCHAs are like the web’s bouncers—keeping out the riffraff so we can all enjoy it. For proxy fans, they’re a puzzle worth solving. With the right tricks (and a little patience), you can glide past them like a pro.
GoProxy offers high purity residential proxies for your activities. Sign up today to get a 7-day free trial! For scale operations, you can choose our unlimited residential proxy plans. Really unlimited traffic, and reasonable pricing. 1-Hour Trial for only $20 – Contact Us to Activate!
< Previous
Next >
 Cancel anytime
Cancel anytime No credit card required
No credit card required